Where the outstations on your system can use either of two direct channels to communicate with the server, you can configure the outstations to be in a shared outstation set that uses either of the available channels for communications. The outstations in a shared set do not all have to use the same channel at any given time.
In direct shared communication set-ups, the efficiency of data transfer is maximized as the load is shared between the two available channels, rather than all communications being via one of the channels. However, if ClearSCADA detects a fault with one of the channels, all communications will take place via the alternate channel.
When configuring a shared communication set-up, you should aim to distribute the outstations evenly across the channels, taking into account any outstations that are fixed to either channel. This will help to ensure that the channels do not become overloaded, and help provide the most efficient communications between the server and the outstations.
Providing that:
- The two channels are completely separate (with no commonality anywhere along the network)
and:
- The driver and remote device support such a feature
you can configure each shared outstation to use the heartbeat polling feature. When heartbeat polling is enabled, the ClearSCADA server automatically sends a heartbeat pulse to the outstation via the channel that is not in use. This checks that the shared outstations can communicate via their alternate channel (that is, the channel that they are not currently using for communications). Use the Heartbeat section on an Outstation Form’s Shared tab to specify whether heartbeat polling is required (see Poll Outstations on the Other Channel). Use the Reestablishment Interval field on the Scan Parameters tab of the Direct Channel Form (see Establish Communications with Failed Outstations) to specify the rate at which any heartbeat pulses are sent.
Example:
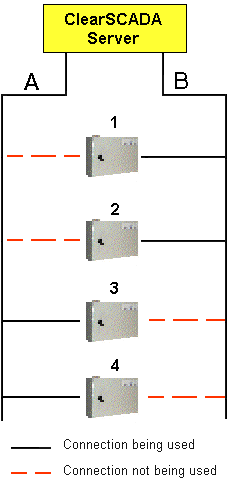
In this setup, each outstation is connected to both of the direct channels (Line A and Line B).
Outstations 1 and 2 are using Line B to communicate with the ClearSCADA server, whereas outstations 3 and 4 are using Line A.
This even distribution of outstations helps to prevent either of the channels becoming unnecessarily overloaded, and helps provide the most efficient communications between the ClearSCADA server and the outstations.