You can use Data Grids to add ‘custom’ tables to your database. Data Grids are not general purpose tables in which to store user data. Instead, Data Grids are used to collate, organize and summaries data from elsewhere in the database, in a tabular format that can be queried from, for example, a List or a Report. (If you require general purpose tables for storing data, consider using Data Tables (see Configuring Data Tables) as opposed to Data Grids.)
NOTE: These should not be confused with standard tables that are based on classes. For information on tables within the database, see the ClearSCADA Guide to the Database.
A Data Grid’s table consists of user-defined fields and a user-defined number of records. Each cell in the table contains an expression that calculates a value. The expression can simply map a value from an item in the database, be a simple literal (constant) value, or a more complex calculation.
You can then configure, for example, a Report, to access the Data Grid’s table, in order to display the results of each calculation.
Operators can display a Data Grid’s table as a List and navigate and sort the data in that List.
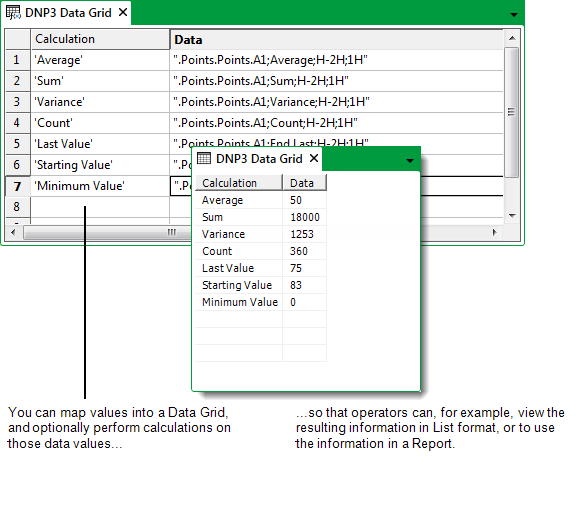
A Data Grid is a document (as is a Mimic, or a Trend) and as such is configuration, as opposed to data. Therefore, by changing the content of a Data Grid, you are changing its configuration.
To create and configure a Data Grid, you need to:
- Add a Data Grid.
- Configure the Properties on the Data Grid Form.
- Edit a Data Grid.
- Specify the Data Grid Size.
- Add an Entry to a Data Grid.
- Repeat step 5 for any further entries in the Grid.
- Save the configuration.
You can then, if required, use the Data Grid’s table in a Report (see the ClearSCADA Guide to Crystal Reports), or display the data in List format (see Display the Data on a Data Grid, Data Set, or Data Table in List Format in the ClearSCADA Guide to Lists).