Use the Event Journal tab on the Configure the Properties of the Root or System Group to enable or disable and define a warning limit for the number of Event Journal records that you expect to created per hour. In addition you can set the maximum number of records stored in a granule. Once a granule reaches the maximum size all further records for the granule are discarded.
Use the following fields to enable or disable and define the Event Journal record limits:
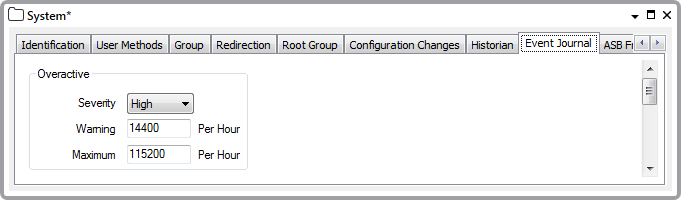
- Severity—Use the Severity combo box to select the Defining Severities. This is the severity of the alarm that you want ClearSCADA to display in event messages when the number of records created per hour reaches the number defined in the Warning and Maximum fields. You can disable the alarms by setting the Severity to None, in which case the Warning field is grayed out.
- Area of Interest—This field is only displayed if the Area of Interest feature is enabled on your system. Use the field to specify the Area of Interest with which overactive alarms are to be associated (see Assign a Different Area of Interest to an Item's Alarms and Events in the ClearSCADA Guide to Core Configuration).
- Warning—Enter the number of Event Journal records per granule per hour that raise a warning alarm. If the number of records in an individual granule reaches this number an alarm is raised to indicate that the granule is overactive. The minimum value you can enter is 500 records. The default value is 14,400 records/hour (4 records/second for an hour).
This default is provided to avoid false alarms and data loss on large systems.
For this feature to be effective you need to specify values appropriate for your system, to avoid problems before a warning is generated.
The Warning alarm message indicates which granule is overactive including both the time and the filename.
"Too many event journal records (# records in hour beginning <time>) file <filename>"
When an alarm is triggered, the alarm source indicates which stream contains the overactive granule (if streams are enabled).
"Event Journal (Stream #)"
NOTE: The Warning field is unavailable and grayed out if the Severity is set to None.
- Maximum—Enter the maximum number of Event Journal records per granule per hour that can be logged. If the number of records in an individual granule reaches this number an alarm is raised to indicate that the granule has reached the maximum value and no more events will be logged for the objects in this stream for the remainder of this period. The minimum value you can enter is equal to the Warning number of records or 500 if alarms are disabled. The default value is 115,200 records/hour (32 records/second for an hour).
This default is provided to avoid false alarms and data loss on large systems.
For this feature to be effective you need to specify values appropriate for your system, to avoid problems before a warning is generated.
Lowering the maximum number of records below the size of existing granules prevents any further records being added to those granules, it does not affect the existing records in those granules.
The Maximum alarm message indicates which granule was overactive and is now full including both the time and the filename.
"Too many event journal records, granule is full (# records in hour beginning <time>) file <filename>"
When an alarm is triggered, the alarm source indicates which stream contains the overactive granule (if streams are enabled).
"Event Journal (Stream #)"
NOTE: If the Severity field is set to None, no alarm is raised when the Maximum number of records is reached.
NOTICELOSS OF DATA
When a granule reaches the specified maximum size all further records for the granule are discarded. This will result in the loss of data. To help prevent loss of data, you need to set appropriate maximum valuesFailure to follow these instructions can result in loss of data
When Event Journal data files (granules) become overactive:
- Review the events list to determine which object(s) are generating large numbers of messages.
- Check for any automated processes (for example, logic programs) that are performing any actions repeatedly.
- Check or change the stream size (so that fewer objects per stream are generated), see Define the Stream Size for Maximum Performance.