Use the Historian tab on the Configure the Properties of the Root or System Group to enable or disable and define a warning limit for the number of historic data records that you expect to created per hour. In addition you can set the maximum number of records stored in a granule. Once a granule reaches the maximum size all further records for the granule are discarded.
NOTE: The settings in the tab are only used if Historic Data is enabled, see Enable or Disable Historic Data.
Use the following fields to enable or disable and define the Historic Data record limits:
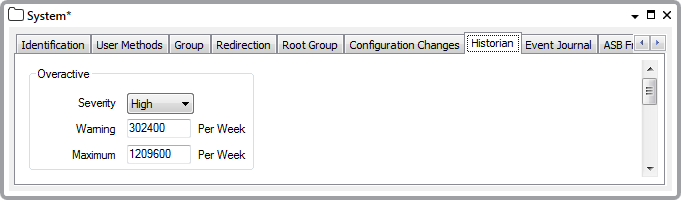
- Severity—Use the Severity combo box to select the Defining Severities. This is the severity of the alarm that you want ClearSCADA to display in event messages when the number of records created per week reaches the number defined in the Warning and Maximum fields. You can disable the alarms by setting the Severity to None, in which case the Warning field is grayed out.
- Area of Interest—This field is only displayed if the Area of Interest feature is enabled on your system. Use the field to specify the Area of Interest with which overactive alarms are to be associated (see Assign a Different Area of Interest to an Item's Alarms and Events in the ClearSCADA Guide to Core Configuration).
- Warning—Enter the number of historic data records per granule per week that raise a warning alarm. If the number of records in an individual granule reaches this number an alarm is raised to indicate that the granule is overactive. The minimum value you can enter is 500 records/week records. The default value is 302,400 records/week (30 records/minute for a week).
This default is provided to avoid false alarms and data loss on large systems.
For this feature to be effective you need to specify values appropriate for your system, to avoid problems before a warning is generated.
The Warning alarm message indicates which granule is overactive including both the time and the filename.
"Too many event historic data records (# records in week beginning <time>) file <filename>"
When an alarm is triggered, the alarm source indicates which point/accumulator, aggregate and data type contains the overactive granule.
"<name>.<aggregate>(<data type>)"
The Warning field is unavailable and grayed out if the Severity is set to None.
- Maximum—Enter the maximum number of historic data records per granule per week that can be created. If the number of records in an individual granule reaches this number an alarm is raised to indicate that the granule has reached the maximum value and no more data will be logged for the point/accumulator for remainder of this period. The minimum value you can enter is equal to the Warning number of records or 500 if alarms are disabled. The default value is 1,209,600 records/week (2 records/second for a week).
This default is provided to avoid false alarms and data loss on large systems.
For this feature to be effective you need to specify values appropriate for your system, to avoid problems before a warning is generated.
The Maximum alarm message indicates which granule was overactive and is now full including both the time and the filename.
"Too many event historic data records, granule is full (# records in week beginning <time>) file <filename>"
When an alarm is triggered, the alarm source indicates which point/accumulator, aggregate and data type contains the overactive granule.
"<name>.<aggregate>(<data type>)"
If the Severity is set to None, no alarm is raised when the Maximum number of records is reached.
NOTICELOSS OF DATA
When a granule reaches the specified maximum size all further records for the granule are discarded. This will result in the loss of data. To help prevent loss of data, you need to set appropriate maximum valuesFailure to follow these instructions can result in loss of dataOnly data files (granules) in the Raw and Suppression historic data types support overactive alerting. Data files (granules) in the Modified and Annotation historic data types do not.
When data files (granules) in the Raw and Suppression historic data types become overactive:
- Check or change deadband and/or persistence settings to reduce the amount of historic data that maybe generated by a fluctuating point value/state (see the relevant driver guide for more information).
- Check and/or change the frequency of the periodic updating of a point.
- Check for a faulty outstation that may be generating 'bad' data, for example, repeatedly reporting the same data.
Further Information
Historic data categories (including Raw and Suppression): see Historic Data Types and Streams in the ClearSCADA Guide to Server Administration.