You need to set the limits for each counter-type point so that when the value of the point rises above the normal range of values, a suitable alarm is raised or event is logged. On many drivers, the driver calculates the value of the counter point from the data that it retrieves from the outstation. This data often comprises an indication that another counter-type event (‘tick’) has occurred. From this information, the driver calculates the running total, or value, of the counter-type point.
To configure the limits of a counter-type point, you need to access the <Point Type> tab of the relevant type of Counter Point Form.
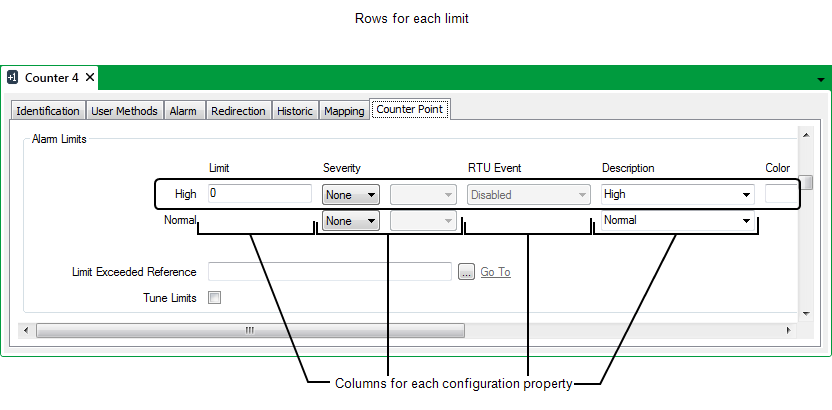
The Alarm Limits section has a row of fields for each limit. The fields are arranged in columns, and are used for defining the configuration properties of each limit. The figure above shows the types of limit that are available for counter-type points on many drivers. Some counter-type points have different limits to those shown above (see Counter-Type Points with Different Limits).
Use the Alarm Limits to define limits that indicate notable changes in operating condition of the plant. By default, many counter-type alarm limits are High-High and High. You can specify whether a point rising past these limits logs an event or raises an alarm.
The Normal state defines the usual operating range for the plant. You can choose whether to log an event whenever the point returns to this state. The Normal state operating range is between zero and the High alarm limit.
The range of limits forms a scale.
Where the counter-type point has only High and High-High limits, the range of limits form a scale, as follows:

Example:
A counter point is used to monitor the amount of electricity that is used each day. An event is logged if power consumption rises to 15kWh/day, and an alarm is raised if power consumption is deemed too high (18kWh/day or more).
The counter point has two alarm limits and has been configured to have these properties:
High-High: 18 kWh (Alarm)
High: 15 kWh (Event)
Normal
The value of the counter point is calculated over a one-day period.
When the value of the counter point is below 15 kWh, it is deemed to be in its usual operating state.
From normal operating conditions, if the point rises to 15 kWh or above, an event is logged to indicate that the point value has risen to the High state.
If the point value continues to rise, and reaches 18 kWh or above, an alarm is raised, to indicate that the point value has risen to the High-High state.
If the point value then drops below 18 kWh, the High-High alarm is cleared. This situation occurs if the point value is in the High-High state when an End of Period (EOP) Reset occurs, or the point is Initialized.
In this particular example, an End of Period Reset occurs automatically at the end of each day. When a Reset occurs, the driver updates the End of Period value with the total counter value for the day that is just ending, then resets the current value of the point back to zero, ready to accumulate the value for the day that is just starting.
Further Information