Use the fields within the Algorithms section of the Security tab to specify which HMAC and Key Wrap algorithms this particular outstation uses.
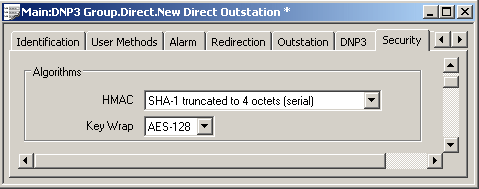
- HMAC—Specify which Hash-based Message Authentication Code (HMAC) algorithm the outstation is to use when:
- responding to challenges sent by ClearSCADA
- issuing Aggressive Mode responses to ClearSCADA. (This only applies if the outstation is configured to issue, and ClearSCADA is configured to accept, Aggressive Mode responses (see Specify Whether Aggressive Mode is Used).)
- Use the combo box to display a list of supported HMACs. We recommend that you select the largest HMAC supported by the DNP3 outstation and appropriate to the type of communications being used. In addition to specifying which algorithm the devices are to use, the selected option also determines how each calculated HMAC value is truncated before being inserted into each message. (A SHA-1 value is 20 octets long before truncation; a SHA-256 value is 32 octets long before truncation.)
- The outstation will generate an ‘HMAC Algorithm Not Permitted’ diagnostics message should it receive a challenge using an HMAC algorithm that it does not support. Should this occur, ClearSCADA will revert to using the HMAC-SHA1 algorithm for further challenge requests.
- Key Wrap—ClearSCADA uses this Key Wrap algorithm to encrypt the Session Keys during a Session Key Change, using a pre-shared Update Key. The algorithm also determines the length of Update Key. ClearSCADA supports a single Key Wrap algorithm, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) AES-128. The AES-128 algorithm requires a 128-bit Update Key, comprising 32 hexadecimal digits.
- During a Session Key Change, the outstation determines which Key Wrap algorithm ClearSCADA is to use for the Session Key Change. Should the outstation request an unsupported Key Wrap algorithm, ClearSCADA will send a ‘Key Wrap Algorithm Not Permitted’ error to the outstation. If this occurs, the outstation has to revert to using the mandatory Key Wrap algorithm AES-128.