ATTENTION: Ensure that you Specify the Outstation Type before configuring the properties on the Ports section of the Outstation Type tab.
Use the fields within the Ports section of the Outstation Type tab to specify the configuration of the serial ports on the SCADAPack E outstation. The number of ports and configuration fields vary, depending on the Outstation Type that is specified at the top of the tab (see Specify the Outstation Type).
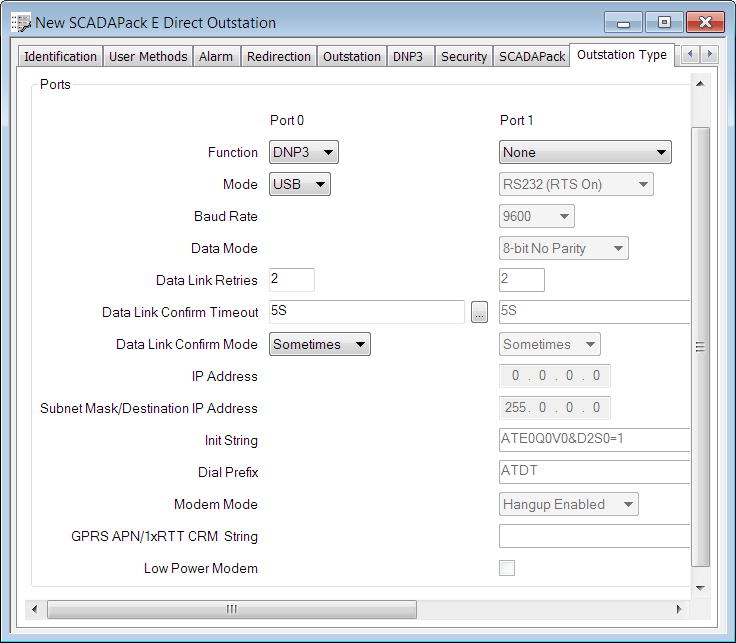
This section details the most common SCADAPack E outstation port settings. For a complete description of the available port settings, see the SCADAPack E Configuration Technical User and Reference Manual, and the SCADAPack E Communication Interfaces Technical User and Reference Manual.
NOTE: Although ClearSCADA is capable of setting the outstation’s port configuration by downloading the outstation’s configuration, ClearSCADA first has to be able to communicate with the outstation. To enable this, use the E Configurator to initially configure one of the outstation’s ports and its DNP3 address, to allow ClearSCADA to communicate with it.
- Function—Use the combo box to specify the function of this port. The options vary, depending on the Outstation Type and the port number, and include a combination of the following:
- None—The port is not used.
- ISaGRAF—The port is used to locally connect ISaGRAF Workbench PC software. This software can be used to download or debug ISaGRAF applications.
The port also has limited Modbus support for a SCADAPack E outstation that acts as a Modbus Slave, and also supports Command-line Shell. For further information, see the SCADAPack E ISaGRAF Technical User and Reference Manual.
NOTE: Only one port may be assigned the ISaGRAF function.
- DNP3—The port is used to communicate with other DNP3 devices. These may include devices local to the outstation, such as actuated valves, other SCADAPack E outstations on the network, and ClearSCADA.
- Cmd Line—The port is used for Command Line diagnostics. You can connect to this port using an ASCII Terminal Emulator to send commands and view diagnostic messages.
NOTE: Only one port may be assigned the Cmd Line function.
- PLC Device—The port is used to communicate with a PLC, for example if you are using the SCADAPack E outstation as a Modbus Master.
- ISaGRAF User—The port enables an ISaGRAF User application that is running in an outstation to send and receive data. This functionality is typically used to create simple device drivers (such as alphanumeric displays). See the SCADAPack E ISaGRAF Function Block User and Reference Manual for further information.
- ISaGRAF 2—The port supports the same functionality as a standard ISaGRAF port (see above), except for the ‘Command Line’ and ‘Diagnostics’ shell commands. This second ISaGRAF port allows for simultaneous ISaGRAF/Modbus communications on dual ports.
- SCADAPack ES Remote I/O—Available if the Outstation Type is set to SCADAPack ES, SCADAPack ER-P600, SCADAPack ER-P620, or 386 eNET. The port is used to communicate with a SCADAPack ES outstation, which provides additional I/O to this SCADAPack E outstation.
If this port function is selected, you need to Configure SCADAPack ES Remote I/O Properties. A DNP3 SCADAPack ES Remote IO item will be required in the ClearSCADA database, to represent the I/O module (see Configuring I/O Expansion Cards and Modules).
- PPP/TCPIP—The port is used for TCP/IP communications. The port can be used for any enabled TCP/IP Service (see Enable TCP/IP Services) and DNP3.
If this port Function is selected, you need to enable and Configure DNP/IP Parameters.
- TCP Service—The port is used to provide a terminal-server like TCP serial interface. If this port function is selected, you need to:
- Enable the outstation’s TCP/IP functionality (see Enable or Disable TCP/IP Functionality).
- Configure TCP Service Port Properties.
- Modbus Slave—The port is used to communicate with a Modbus Master device, using the Modbus protocol. If this port function is selected, you need to Configure Modbus Properties.
Where TCP/IP communications are used, see the following sections:
- DNP VT Service—The port is used to send and receive serial data between a SCADA Master (ClearSCADA) and a device connected to this port using DNP3 Virtual Terminal Objects (see Configuring DNP3 Virtual Terminals in the ClearSCADA Guide to the DNP3 Driver).
If the DNP3 master driver is used for routing comms, using a Virtual Terminal, you need to Configure a DNP3 VT Service Port Master and Configure a DNP3 Virtual Terminal. The Virtual Terminal Number on the DNP3 Virtual Terminal Form has to correspond to the Port number being used on the SCADAPack E outstation.
- IEC 60870-5-103 Master—Available for Outstation Types other than the 386 eNET. The SCADAPack E outstation is an IEC 60870-5 Controlling Station (SCADA master) and obtains data from IEC 60870-5 Controlled Stations (Slave devices) on this port, using the IEC 60870-5-103 protocol.
Be aware that a SCADAPack E outstation requires additional licensing in order to provide IEC 60870-5-103 master functionality.
- IEC 60870-5-101 Slave—Available for Outstation Types other than the 386 eNET. The port is used to communicate with an IEC 60870-5 Controlling Station (SCADA master), using the IEC 60870-5-101 protocol.
- NTP GPS Receiver—The port is connected to a GPS receiver. This enables the outstation to act as an NTP time server and provide an accurate time source.
- SLIP and CSLIP—SLIP (Serial Line Internet Protocol) is a protocol that supports IP communication over serial links. CSLIP (Compressed SLIP) is a version of SLIP that compresses data for transmission. While older than PPP, these protocols are still in use in some lower speed serial networks. SLIP and CSLIP are point-to-point protocols for connecting two IP devices. Unlike PPP there is no connection negotiation. The local and remote IP addresses of the devices are set by user configuration, and must be consistent in both devices on the link.
SLIP and CSLIP frame IP messages over serial communication, so the end of messages can be clearly identified. SLIP simply provides framing. CSLIP also compresses the TCP/IP header to improve performance on slow links.
These protocols permit more robust handling of the communication packets.
- Modbus Master (Modbus RTU)—The SCADAPack E outstation uses the port to communicate with a Modbus slave device.
- Conitel Slave—Only available on Ports 5 to 8 when a SCADAPack ER-P620 Outstation Type is specified. The port is used to communicate with a SCADA master using the Conitel 2020 protocol.
- Mode—Use the combo box to specify the mode in which a port is operating. The options vary, depending on Outstation Type and the port’s Function (see above). For most ports, the possible options are:
- RS232 (RTS On)
- RS232 (RTS Off)
- RS232 (RTS Keyed)
- RS422
- RS485 2 Wire
- RS485 4 Wire Master
- RS485 4 Wire Slave
- Hayes Modem
- Hayes Pool
- GPRS (only available on ports on which the Function is specified as PPP/TCPIP)
- 1xRTT (only available on ports on which the Function is specified as PPP/TCPIP)
- FSK Radio (only available on Port 3 on a 386 eNET)
- FSK Landline (only available on Port 3 on a 386 eNET)
- SMR Radio (only available on Port 3 on a 386 eNET)
- X.29 (only available on ports on which the Function is specified as DNP3. Limited to certain ports on some types of SCADAPack E outstation.) Use the properties on the outstation’s X.29/TC Comms tab to Specify the X.29/TC Comms Properties.
NOTE: Changing a port between RS232 and RS422 or RS485 may require a hardware modification. See the SCADAPack E Communication Interfaces Technical User and Reference Manual for details.
If a SCADAPack 330E/334E, or SCADAPack 350E/357E Outstation Type is specified, Port 0, if used, has its Function limited to DNP3 and its Mode limited to USB. Additionally, with a SCADAPack 350E/357E Outstation Type, Port 1’s Mode is limited to RS485 2 Wire.
- Baud Rate—Displayed when applicable. Use the combo box to specify the baud rate used for transferring data via the port.
NOTE: Some SCADAPack E models have restrictions on the available ports, modes, functions, and baud rates. See the SCADAPack E Operation Reference Manual for details on these limitations.
ATTENTION: If one of the outstation’s serial ports is being used to communicate with ClearSCADA, the configuration of the port in the ClearSCADA DNP3 SCADAPack E outstation has to match the configuration of the Channel item that ClearSCADA uses to communicate with that outstation. If these configurations differ, communications to the outstation will be lost when ClearSCADA downloads the configuration to that outstation.
- Data Mode—Displayed when applicable. Use the combo box to specify the number of data bits used to transmit each byte of data and the parity. The options vary, depending on the port’s Function, but comprise a combination of the following:
- 8-bit No Parity
- 8-bit Even Parity
- 8-bit Odd Parity
- 7-bit Even Parity
- 7-bit Odd Parity.
- Data Link Retries—see Configure Data Link Layer Properties.
- Data Link Confirm Timeout—see Configure Data Link Layer Properties.
- Data Link Confirm Mode—see Configure Data Link Layer Properties.
- IP Address—Applies only if the Function of the port is set to PPP/TCPIP. Use to specify the IP Address of the port.
- Subnet Mask/Destination IP Address—If the Function of the port is set to PPP/TCPIP, use this field to specify the Subnet Mask of the port. If the Function of the port is set to CSLIP or SLIP, use this field to set the Destination IP Address.
- Init String—Applies only if the port Mode is set to Hayes Modem or Hayes Pool. Use to specify the initialization string that is sent to the modem on start-up and at 60 second intervals to check the health of the modem.
- Dial Prefix—Applies only if the port Mode is set to Hayes Modem or Hayes Pool. Use to specify the prefix that is added to the phone number, in order to force the modem to dial the required number. Specify the actual telephone number in the DNP Route Table (see Add and Configure the Entries in a DNP Route Table).
- Modem Mode—Applies only if the port Mode is set to Hayes Modem or Hayes Pool. Use the combo box to specify whether the outstation maintains a permanent connection with the remote device, or whether it hangs up the modem if no transmissions occur over the port for a specified period of time. Choose from:
- Hangup Enabled—The default option. The modem hangs up once no communications traffic has occurred over the port for a specified time. Use the Modem Inactivity Timeout field within the Modem Parameters section of the SCADAPack tab to specify the timeout (see Configure the Modem Parameters).
- Hangup Disabled—The SCADAPack E outstation maintains a permanent connection with the remote device, until the remote device disconnects.
- GPRS APN/1xRTT CRM String—Applies only if the port Mode is set to GPRS or 1xRTT. General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a service that allows information to be transmitted across a GSM mobile telephone network. 1xRTT is a Radio Packet service that allows information to be transmitted across a CDMA mobile telephone network.
Specify the network-specific setup string that the outstation is to send to the GPRS or 1XRTT modem when the outstation is establishing a connection.
Consult your network operator for the required string.
Example:
"AT+CGDCONT=1, "IP", "<network name>""
Use the fields in the Port Configuration section of the SCADAPack tab to specify the PAP or CHAP username and password that enable access to the GPRS or 1xRTT network (see Configure the DNP Route Table and Modem Authentication Properties).
- Low Power Modem—Applies only if the port Mode is set to Hayes Modem or Hayes Pool.
Select the check box if the outstation uses a low power modem. When selected, the Data Terminal Ready (DTR) signal is asserted by the outstation whenever the outstation needs to communicate via the port. Specify the required DTR Delay Time on the Modem Parameters section of the SCADAPack tab (see Configure the Modem Parameters).
Clear the check box if the modem is not set to operate in low power mode.