| Function Name |
MUL (Multiply) |
|---|---|
|
ST Operator |
* |
|
Description |
Multiplies the inputs to provide the output. |
|
Arguments |
Input 1 - Input n {ANY_NUM} For more information on the data types for the inputs and outputs, see Data Type Hierarchy. |
|
Returns |
Output {Same data type as input} The Output = Input 1 x Input 2 x Input 3 and so on. |
Example:
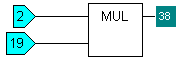
Function Block Diagram - MUL:
The output is the result of the top input multiplied by the bottom input. So, if the top input is 2 and the bottom input is 19, the output is 38 (2 x 19=38).
ST Program - MUL:
The MUL function is used to provide the result of Input 1 divided by Input 2:
Output := Input 1 * Input 2;
Where Output, Input 1 and Input 2 are defined as variables earlier in the ST program. In this case, let's assume Input 1 is 60 and Input 2 is 10. The DIV function returns 600 as 60 x 10=600 (the asterisk * represents the MUL function).
When there are more than 2 inputs, it is more efficient to use the following syntax:
- Output := MUL (Input 1, Input 2, Input 3, Input 4 and so on);
For example:
- Output := MUL (12, 4, 32, 6);
This would return 9126 as this is the result of 12 x 4 x 32 x 6.