| Function Name |
OR |
|---|---|
|
Description |
Outputs a True value when any of its inputs are True. |
|
Arguments |
Input 1 to Input n {ANY_BIT} For more information on the data types for the inputs and outputs, see Data Type Hierarchy. |
|
Returns |
Output {BOOL} If any of the inputs is True, the output is True. The output is only False if each of the inputs is False. |
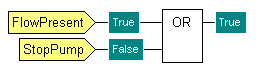
Example:
Function Block Diagram - OR:
An OR function has 2 inputs - Input 1 is from a flow sensor and is named 'FlowPresent' and Input 2 is from a Pump control and is named 'StopPump'. When the function receives a True input from either 'FlowPresent' or 'StopPump' it outputs a True value. The output is only False if all of its inputs are False.
ST Program - OR:
The OR function is used to provide a Boolean value that is True if any of its inputs are True. The syntax for an OR function in an ST Program is:
- Output := OR (Input 1, Input n);
Where Output, Input 1 and Input n are defined as variables earlier in the ST program. Each input is separated by a comma and is a Boolean. The Output value is also a Boolean.