Each server in a multi-server architecture monitors the other servers in the architecture to check that the hardware, software and network connections are working correctly. To do this, each server performs up to four checks:
- A TCP/IP server software to server software check
- An ICMP server to server hardware check
- Up to two additional ICMP server to server hardware checks.
For more information on these checks, see Define the ICMP Monitor Settings for a Server.
During each check, a server attempts to check the status and role of the other servers in the architecture. It also requests a response from the other server. If the connection is not made or a response is not received within a specified amount of time, the other server becomes isolated and the appropriate action is initiated (as defined in the Action on Isolated setting, Define what Action Should be Taken when a Server Becomes Isolated).
You can configure the amount of time a server will wait for a connection to another server and how long it will wait for a response to a request. To do this, you need to use the System Configuration>Partners settings in the Server Configuration Tool. The Standby tab of the Partners settings has a Monitor section that contains the monitoring Connect Timeout and Request Timeout settings.
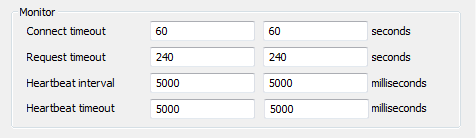
- Connect Timeout—Define the amount of time, in seconds, that the server will wait for a monitor connection to occur. If there is no monitor connection between the server you are configuring and the other server after the defined Connect Timeout, the other server becomes isolated and the appropriate action is initiated (as defined in the Action on Isolated setting, Define what Action Should be Taken when a Server Becomes Isolated).
The default setting is 60. - Request Timeout—Define the amount of time, in seconds, that the server will wait for a response from the other server(s). If there is no response after the defined Request Timeout, the other server becomes isolated and the appropriate action is initiated (as defined in the Action on Isolated setting, Define what Action Should be Taken when a Server Becomes Isolated). The default setting is 240.
- Typically, the default settings of 60 and 240 seconds are appropriate. To detect faults that occur more quickly, use the Heartbeat Interval (see below). Be aware that if the Connect timeout is too short, a server may become isolated before it has had time to process a response to a request (or complete the connection establishment process).
- Heartbeat Interval— Define the interval time, in milliseconds, for heartbeat poll requests between this server and related Hot Standby servers. This could be:
- A Permanent Standby's related Hot Standby servers (for which it depends for database updates) or
- A Hot Standby server's polling of other Hot Standby servers from which the server chooses a Main.
Each server can have different settings. If there is no response to the heartbeat poll from a partner server after the defined Heartbeat timeout, ClearSCADA will determine that the polled server has failed. (That is, there is either no ClearSCADA service running or the server host is unreachable). The default setting is 5000.
- Heartbeat timeout— Define the amount of time, in milliseconds, that the server will wait for a heartbeat response from the other server(s). The default setting is 5000.
The Heartbeat uses a dedicated channel that allows you to set short intervals and timeouts to speed up the fail over procedure. Appropriate values will be dependent on desired fail over time and network architecture.
NOTE: If you change the value in any of these fields, you will need to restart the ClearSCADA server for the change to take effect.