You can use the Channels section of the ClearSCADA Server Configuration Tool to define the duration of the delay between consecutive calls on a PSTN channel. A delay may be required when using network connected serial ports, such as a Comtrol DeviceMaster. With such setups, delays can be needed due to latency when reporting the reply from a modem to a hang-up command.
When a call has completed, the driver sends a hang-up command to the modem. The completion of the hang-up can be signalled in two ways - the reply from the modem and (with a fully wired cable) the carrier detect signal changing to Low. With a network connected serial port, there can be delay between the driver receiving the reply from the modem and the carrier detect signal change. This can cause a problem if there is another call pending when the first call completes, as the driver can start the new call and then receive the reply from the modem to the hang-up command. The reply from the modem is then mistakenly handled as being related to the new call, which causes the call attempt to fail with a 'No carrier' error.
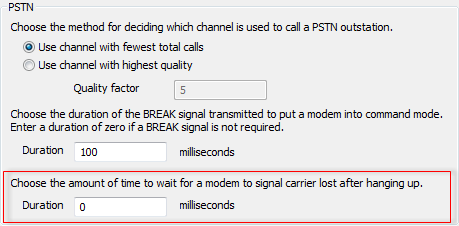
To avoid this problem, you can define a delay that is applied after hanging up the modem (and so allow time for the modem reply to be received). The duration of this delay will vary depending on the amount of latency on your network, but can be between 200ms and 5000ms.
To define the duration of the delay:
- Access the ClearSCADA Server Configuration Tool (see Accessing the ClearSCADA Server Configuration Tool).
- Expand the Global Parameters branch of the tree structure.
- Select Channels to access the Channels section.
- Use the lower Duration field in the PSTN box to define the duration of the post hang-up delay.
-
- Close the ClearSCADA Server Configuration Tool to apply the changes (or select another branch if further server configuration is required).
When you have finished defining the duration settings, you can either configure other Channels settings:
- Define the Settings for Channel Scanning Statistics Trends.
- Define how a PSTN Channel is Selected for Communications.
- Define the Settings for COM Ports and TCP/IP Connections.
Or:
- Continue with the server configuration. If you are unfamiliar with the server configuration process, we recommend that you proceed to learn about Driver Settings.