Triple Standby server architectures are similar to Hot-Standby pair architectures except that instead of there being one Standby server, there are two. As with Hot-Standby Pair arrangements, one of the servers is recognized as the Main server, with the other servers being Standby servers. Clients and plant can be connected to any of the servers, but the data they report is sent to the Main server and stored in the Main server’s database. The Main server then updates the databases in the Standby servers so that they match the Main server database.
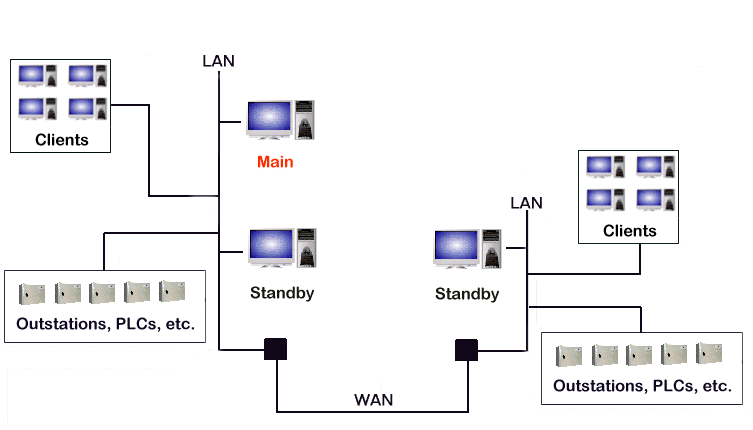
The diagram above shows a possible Triple Standby architecture, where two servers are connected via a LAN and they connect to the third server via a WAN.
Triple Standby architectures provide additional backup in the event of a hardware, software or network failure.
- On systems with dual connections, the server architecture will continue to run as a Triple Standby in the event of the Main server losing its connection with one of the two others. However, this only applies if the two other servers can still connect to each other. As the Main server is unable to use the lost connection, communications to both servers will be made via the healthy connection. This may have an impact on system performance as there will be no load balancing due to there only being one available connection.
- If the Main server loses its connections with both of the other servers but the other servers can still communicate with each other, the Main server will become isolated. The other two servers will arbitrate to determine which of the two is to switch to Main, and they will continue to run as a Hot-Standby Pair until the isolated server is restored. When the isolated server is able to connect to the other two servers, the three servers will arbitrate to determine which server is Main.
ATTENTION: If a Main server goes offline and is restored as the Main server, the data reported while a Standby server was Main may be lost. For example, if Server A has been Main for 10 hours when it goes offline, Server B switches to Main and Server C remains as a Standby. Server A is restored within 2 hours, and as it has been Main for longer than Server B and Server C (in total), it is set to Main and Server B is switched to Standby. The data that was reported to Server B while it was Main may be lost. The data is only retrievable if the outstations or PLCs being used support Windback. For more information, refer to the documentation for your outstations, PLCS etc.
- If the servers are unable to connect, the Standby servers will become isolated and will respond according to their Action on Isolated setting (see Define what Action Should be Taken when a Server Becomes Isolated). Depending on the servers’ configuration, this could result in a Main-Main or Main-Main-Main situation.
When a manual changeover is performed, the Main server will switch to Standby and the Standby server that has been running the longest amount of time will switch to become the new Main server.
NOTE: Multi-server systems (redundancy) require a license and so are only supported by full versions of ClearSCADA.