Most drivers enable ClearSCADA to communicate with outstations and other devices using a permanent direct communications connection.
To understand the basic concepts of a system with direct communications, you need to appreciate the role of each part of the system. This section explains the basics, beginning with the client PC on which you interact with ClearSCADA.
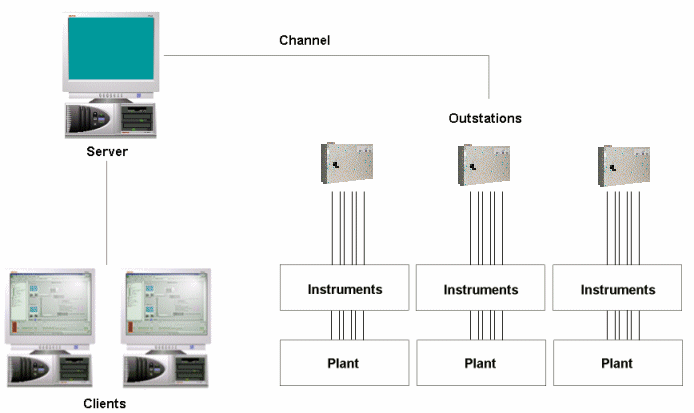
ClearSCADA Client PCs have network connections to a ClearSCADA server. The ClearSCADA Server stores the database and communicates with equipment such as outstations and PLCs. The outstations communicate with the instruments that monitor and control plant. The client PCs interact with plant via the ClearSCADA server and the outstations (see Outstations and Outstation Sets).
NOTE: The term ‘outstation’ is used throughout much of the ClearSCADA documentation as a generic term for devices, such as outstations, RTUs, PLCs, and Data Loggers, that obtain data from measuring instruments or sensors.
Your client PC can either run ViewX (see ViewX Client in the ClearSCADA Guide to ViewX and WebX Clients) or use WebX in a browser (see WebX Client in the ClearSCADA Guide to ViewX and WebX Clients). It uses ViewX or WebX to interact with the ClearSCADA system. When you perform an action or issue a control from a client, the control data is sent from your PC to the ClearSCADA server. Depending on the type of action, the ClearSCADA server either performs the action within the database or sends the data to the outstations.
With direct communications, the ClearSCADA server communicates with the outstations via direct channels (see Channels). This means that there is a continuous connection between the ClearSCADA server and the outstations (see Outstations and Outstation Sets). The direct connections can use cables that are physically attached to the ClearSCADA server and the outstations, or they can be some other form of communications media, such as radio.
Most instruments report a signal to an outstation continuously. The outstation stores a sample from the signal which is then sent to the ClearSCADA server upon request. The ClearSCADA server processes the signal and stores the values in the database.
When an outstation receives a control, it processes the data and sends a signal to an instrument that is connected to the plant. The instrument then operates the plant—for example, a signal could instruct an instrument to close a valve or activate a power on/off switch. (On some systems, the instruments are the plant.)
The database uses points to correspond to the inputs and outputs on an outstation. The inputs receive data from the plant and the outputs send data to the plant. Any values sent to or received from an outstation are stored within the corresponding point item in the database (see Points and Pulse Actions).
NOTE: On most systems, ClearSCADA will be configured to instigate communications with any direct outstations whenever required. On some systems, the communications availability might be restricted on some direct outstations. For example, communications might be limited to Incoming Only (whereby the outstation instigates all communications with ClearSCADA), or Periodic (whereby communications with the outstation is only available for a limited period). For more information, see Specify the Availability of Communications Between the Outstation and ClearSCADA in the ClearSCADA Guide to Advanced Drivers.